As is the case with any other medication, there may be some instances where atorvastatin use is not recommended or usage will have to be adjusted in order to prevent or reduce the risk of negative interactions occurring from other drugs, medical conditions, or even food and drink.
Drug Interactions
According to the FDA, drugs that may interact with Lipitor (atorvastatin calcium) include the following:
- Strong inhibitors of CYP 3A4, such as clarithromycin, a combination of protease inhibitors, and itraconazole
- Cyclosporine
- Gemfibrozil
- Other fibrates
- Niacin (vitamin B3)
- Rifampin or other inducers of cytochrome P450 3A4
- Digoxin
- Oral contraceptives (hormonal birth control pills)
- Colchicine
- Diltiazem
- Do NOT take atorvastatin with red yeast rice
The FDA also states the following information:
| Potential Interacting Drugs | Recommendations |
| Cyclosporine, HIV protease inhibitors (tipranavir plus ritonavir), hepatitis C protease inhibitor (telaprevir) | Avoid atorvastatin |
| HIV protease inhibitor (lopinavir plus ritonavir) | Use with caution and lowest dose necessary |
| Clarithromycin, itraconazole, HIV protease inhibitors (saquinavir plus ritonavir, darunavir plus ritonavir, fosamprenavir, fosamprenavir plus ritonavir) | Do not exceed 20 mg atorvastatin daily |
| HIV protease inhibitor (nelfinavir), Hepatitis C protease inhibitor (boceprevir) | Do not exceed 40 mg atorvastatin daily |
| Other Lipid-Lowering Medications | Use with fibrate products or lipid-modifying doses (â¥1 g/day) of niacin increases the risk of adverse skeletal muscle effects. Caution should be used when prescribing with LIPITOR |
| Digoxin | Requires close monitoring* |
| Oral contraceptives | Norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol values may increase* |
| Rifampin | Must be given at the same time as Lipitor* |
Furthermore, the FDA also states that negative reactions may occur following Lipitor use in the following situations:
- “concomitant use of higher doses of atorvastatin with certain drugs such as cyclosporine and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., clarithromycin, itraconazole, and HIV protease inhibitors)…
- concurrent administration of cyclosporine, fibric acid derivatives, erythromycin, clarithromycin, the hepatitis C protease inhibitor telaprevir, combinations of HIV protease inhibitors, including saquinavir plus ritonavir, lopinavir plus ritonavir, tipranavir plus ritonavir, darunavir plus ritonavir, fosamprenavir, and fosamprenavir plus ritonavir, niacin, or azole antifungals…
- atorvastatin co-administered with colchicine…
- Caution should be exercised if a statin is administered concomitantly with drugs that may decrease the levels or activity of endogenous steroid hormones, such as ketoconazole, spironolactone, and cimetidine”
Please note that these lists may not be complete, and other interactions not listed here may occur.
Atorvastatin and Vitamin D
When most people mention vitamin D, they are referring to either vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and or vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol). Vitamin D is necessary for several bodily functions, such as proper absorption of calcium, which is necessary for strengthening bones. While the exact mechanisms are not understood, some research has found that:
- Certain statins may affect the body’s levels of vitamin D, and
- Interactions may occur when taking statins with vitamin D supplements.
Firstly, it appears that some statinsâlike atorvastatin (Lipitor) and simvastatin (FloLipid, Zocor)â increase blood levels of this vitamin.
Secondly, smaller studies found that vitamin D3 supplementation can decrease the body’s levels of atorvastatin. It’s not just atorvastatin that these supplements affect, either; even the metabolites (chemicals that the body breaks this medication into) are affected. Interestingly, despite this interaction, these same studies found that this combination seemed to boost “cholesterol-lowering activity.”
Larger, more extensive studies are needed to back up this research. That being said, current research suggests that there is a clear interaction between statins and vitamin D.
Atorvastatin and Gemfibrozil
According to the FDA, concomitant (at the same time) use of atorvastatin and gemfibrozil (Lopid) increases the risk of myopathy (disease where muscle fibers malfunction) and rhabdomyolysis (condition where muscle breaks down and releases a harmful protein into the bloodstream).
Atorvastatin and Amlodipine
According to the FDA, amlodipine (Norvasc) may affect Lipitor’s (atorvastatin calcium) pharmacokinetics (how the drug behaves in the body).
Lipitor and Plavix
Plavix (clopidogrel) is a blood thinner that may interact with Lipitor (atorvastatin). Anyone taking Plavix should tell their doctor before taking Lipitor.
Food Interactions
Sometimes the foods and beverages a person consumes can interact with the medications they take.
Food and drink that may interact with Lipitor (atorvastatin calcium) include:
- Grapefruit and grapefruit juice
- Alcohol
- Red Yeast Rice (RISK X: Do not take with atorvastatin)
Please note that this list may not be complete, and that other foods and beverages may interact with this drug.
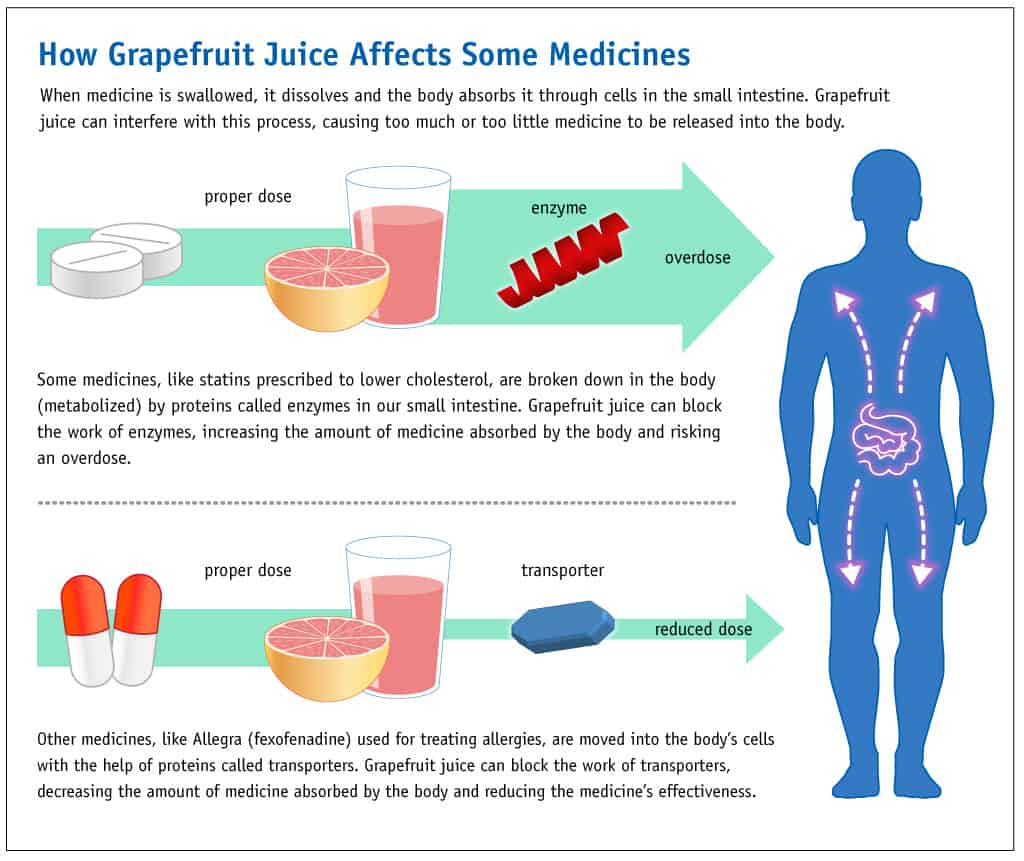
Statins and Grapefruit Juice
Experts advise against eating grapefruit or drinking grapefruit juice when taking statins like Lipitor (atorvastatin calcium).
Why is that, though?
It all has to do with how the body processes atorvastatin. Namely, the body uses the enzyme (special protein) CYP3A4 to break down atorvastatin. Now, components of grapefruit juice inhibit the actions of this enzyme. The result? With this enzyme inhibited, plasma concentrations of statins, such as atorvastatin, can increase. If these levels increase enough, it can cause negative side effects.
Atorvastatin and Alcohol
For more information, please visit our page on atorvastatin and alcohol interactions.
Condition & Disease Interactions
Sometimes certain medications can increase the risk of negative side effects for patients with certain diseases or other medical conditions.
According to the FDA, Lipitor is contraindicated (should not be used) for the following conditions:
- “Active liver disease, which may include unexplained persistent elevations in hepatic transaminase levels…
- Hypersensitivity to any component of this medication”
- Pregnancy
- Lactation
According to the FDA, the following conditions and diseases may also increase the risk of certain side effects:
- “history of renal [kidney] impairment”
- “Patients with Recent Stroke or TIA”
Please note that these lists may not be complete, and there may be other diseases or medical conditions where the use of atorvastatin is not recommended, the usage and dosage must be adjusted, or the patient must otherwise be closely monitored due to increased risk of negative reactions occurring.
Atorvastatin and Pregnancy
For more information, please visit our page on atorvastatin and pregnancy risks.
Atorvastatin and Diabetes
According to the FDA, Lipitor is indicated for (advisable for the treatment of) certain people with type 2 diabetes to reduce their risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Atorvastatin and Hair Loss
Although rare, there are reported cases of alopecia (hair loss) resulting from the use of Lipitor.
Atorvastatin and Weight Gain
Weight gain is an uncommon side effect of atorvastatin. However, it may be a sign of a serious side effect from taking this medication, according to the American College of Cardiology.
Atorvastatin and Muscle Pain
People who experience muscle pain while taking this medication should contact their doctor right away, as it could be a sign of serious side effects: myopathy and rhabdomyolysis.
Lipitor and Memory Loss
According to the FDA, there have been rare instances where someone taking a statin, such as Lipitor, subsequently experiences cognitive side effects like memory loss. Fortunately, these effects are typically not serious and cease when the patient stops taking the medication. Anyone experiencing memory loss while taking Lipitor should contact their doctor to discuss possible next steps.
Lipitor and COVID 19
Because COVID-19âthe illness caused by the novel coronavirus SAR-CoV-2âis so new, researchers are still struggling to understand how certain medications interact with this condition. Some research, though, shows promising results regarding COVID-19 patient outcome and statin use. For example, one study recently published on medRxiv suggests that statin use may help prevent certain elderly individuals from experiencing severe COVID-19 symptoms. Furthermore, there are U.S. clinical trials underway to examine how statins (in combination with other forms of treatment) affect the survival rate of COVID-19 patients.
These findings may come as a surprise to some, as COVID-19 is primarily thought to be a respiratory condition. Recent findings, however, support the idea that COVID-19 affects other parts of the body besides just the respiratory system, including the heart. For instance, one study published in The New England Journal of Medicine reports that autopsies of COVID-19 patients revealed that plenty of other tissues in the body outside of the lungs contained the virus. In fact, several of these autopsies revealed that the virus was inside heart tissues.
It’s important to remember that the results of these studies are not conclusive and, at the time of writing, not all of this research has been peer reviewed. Since experts are still unsure of the role the coronavirus can play in the health of those taking statins, patients should keep taking their prescribed medications unless otherwise directed by a licensed healthcare professional.
Lipitor and Joint Pain
According to the FDA, clinical studies report that many patients experience joint pain as a side effect of taking this drug.
Disclaimer: this article does not constitute or replace medical advice. If you have an emergency or a serious medical question, please contact a medical professional or call 911 immediately. To see our full medical disclaimer, visit our Terms of Use page.




