Also called:
- Acute bronchitis
- Chest cold
- Common cold
- Chronic bronchitis/COPD (chronic bronchitis is a form of COPD)
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (the tubes that carry air in and out of the lungs); it may be acute or chronic. Acute bronchitis is a temporary condition, while chronic bronchitis is a long-term illness.
What is Bronchitis?
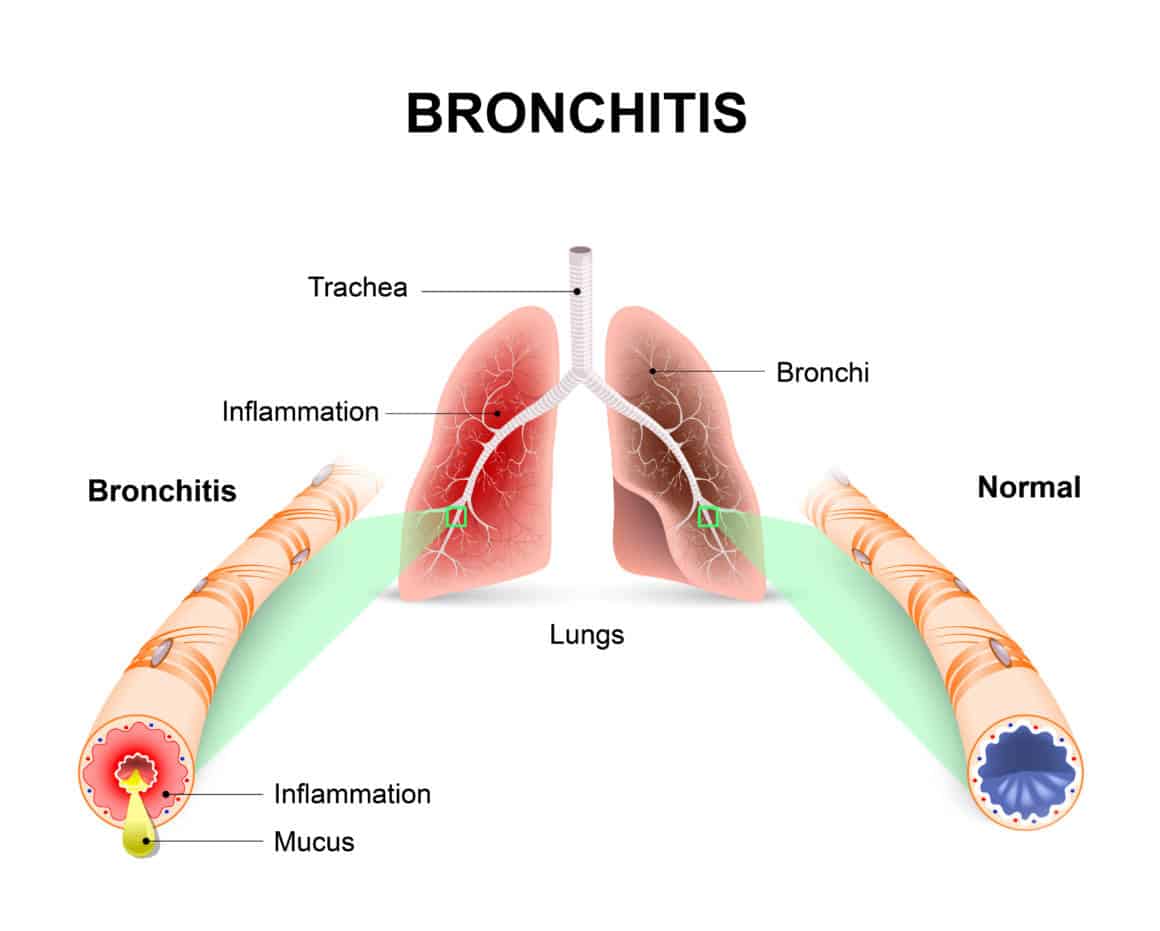
Bronchitis causes swelling and inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which are the air passages that connect the nose and mouth with the lungs. Inflammation of the bronchial tubes can produce mucus in the lungs, which in turn causes a cough. This mucus also makes it more difficult for the lungs to move oxygen in and carbon dioxide out of the body.
How Common is the Condition?
Doctors diagnose approximately 9 million cases of chronic bronchitis in the United States annually, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). That means about 3.6 percent of the nation’s population will typically develop this long-term breathing problem each year. Acute bronchitis affects about 4.4 percent of people each year. Chronic bronchitis is more common in adults over the age of 50, while acute bronchitis is most common in children younger than 5 years.
Disclaimer: this article does not constitute or replace medical advice. If you have an emergency or a serious medical question, please contact a medical professional or call 911 immediately. To see our full medical disclaimer, visit our Terms of Use page.